After a wound is cleaned and free from infection, the body enters the most beautiful stage of recovery — the healing phase. This is the stage where new tissue forms, skin repairs, and strength returns.
Acharya Sushruta described a group of special treatments under Shasti Upakrama that focus on building new tissue, strengthening the body, and supporting natural healing. These methods are still followed in modern medicine, although with different tools.
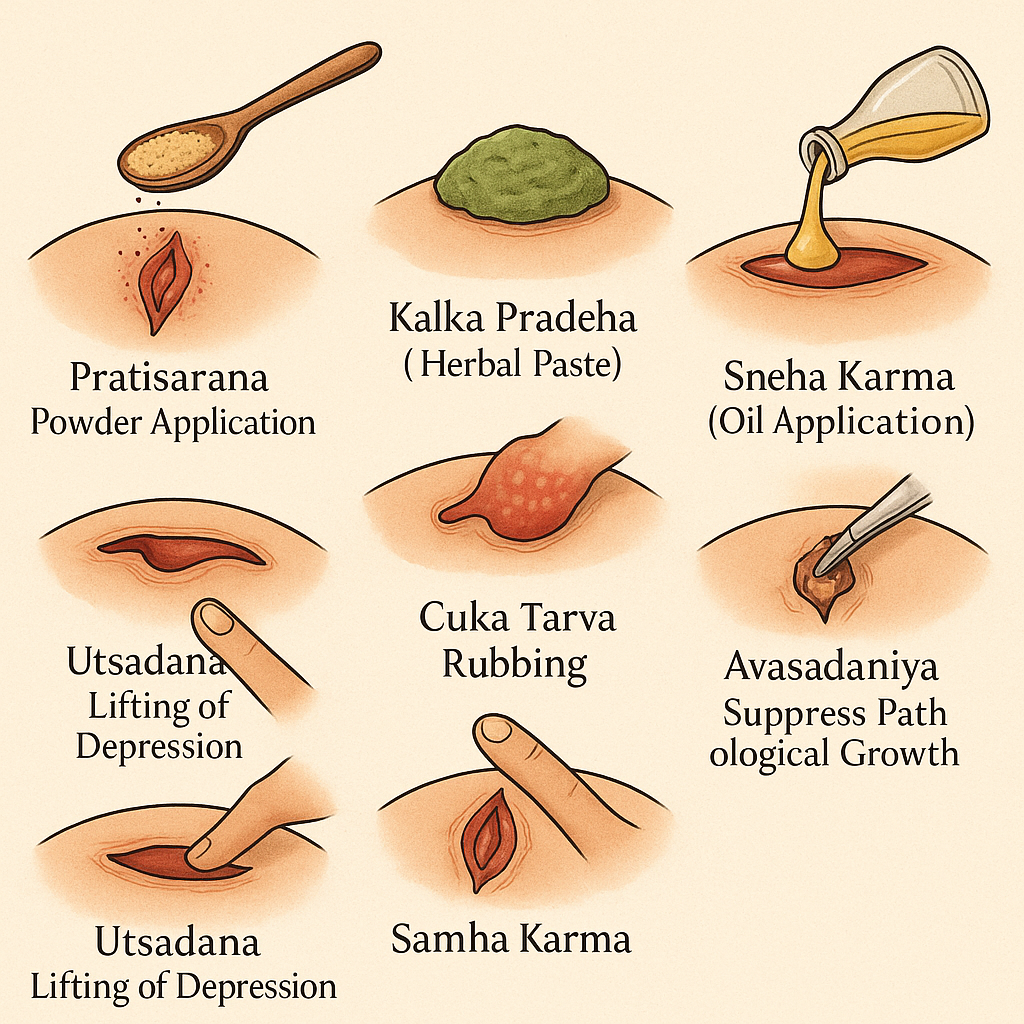
Ropana – Promoting Wound Healing
Ropana means encouraging natural wound healing.
This involves using herbal medicines and proper care to help:
- New skin form
- Wound edges close
- Scars become healthier
Modern example:
Use of healing ointments, regenerative creams, and advanced dressings.
Utsadana – Raising Depressed Wound Area
Utsadana helps when the wound area becomes sunken or weak.
It promotes:
- Tissue growth
- Healthy granulation
- Better blood flow
Modern equivalent:
Use of collagen dressings and growth-promoting wound materials.
Brimhana – Nourishing the Body
Brimhana focuses on internal nutrition and strength.
A well-nourished body heals much faster.
This includes:
- Nutritious diet
- Herbal tonics
- Strength-giving foods
Modern science agrees:
High-protein diets and supplements are used for faster recovery.
Balya – Strengthening Technique
Balya therapies build strength of tissues and muscles.
This is useful for:
- Weak wounds
- Fragile skin
- Elderly patients
Modern comparison:
Use of vitamins, minerals, and tissue-strengthening supplements.
Alepa – Applying Medicinal Paste
Alepa means applying healing pastes over the wound.
These pastes:
- Protect the wound
- Reduce inflammation
- Support tissue repair
Modern version:
Medicated creams, antibiotic ointments, protective gels.
Pradeha – Application of Thick Herbal Layers
Pradeha is thicker than Alepa and stays longer on the wound.
Used to:
- Keep the wound moist
- Increase absorption of medicines
- Speed up tissue repair
Modern example:
Therapeutic poultices and moisture-locking dressings.
Kalka Pradeha – Herbal Plaster Treatment
This involves freshly prepared herbal plasters applied on the wound.
Today, this concept is used in:
- Natural wound packs
- Herbal dressings
- Therapeutic wound wraps
Ksheera Karma – Milk-Based Healing Therapy
Milk has natural soothing and nourishing properties.
In ancient times, milk-based preparations were used to:
- Cool the wound
- Reduce burning
- Improve the softness of tissues
Modern equivalent:
Soothing, moisturising wound creams.
Sneha Pana – Internal Oil Therapy
Sneha Pana means giving healthy oils internally.
Oils nourish:
- Skin cells
- Body tissues
- Healing mechanisms
Modern example:
Omega fatty acids and healthy oils in the diet.
Mamsarasa – Meat Soup Therapy
This therapy focuses on protein-rich soups to build body tissues.
Modern science supports this because protein is essential for:
- Collagen formation
- Cell repair
- Tissue strength
Ksheerapana – Therapeutic Milk Intake
Milk provides:
- Calcium
- Proteins
- Energy
which are essential for rebuilding damaged tissues.
Modern hospitals also recommend milk-based nutrition drinks for wounded or post-surgical patients.
Why This Phase Is Important
This stage is where:
✅ The wound becomes smaller
✅ New tissue forms
✅ Strength returns
Without good nutrition and proper external care, healing becomes slow and weak.
These healing treatments of Shasti Upakrama show that Sushruta understood that true healing happens not only on the wound surface but inside the body as well.
Even today, doctors focus on nutrition, dressings, and tissue support—just like Sushruta taught thousands of years ago.







